Table of Contents
EsiaVoyager mobile application
Installation
The application is available on </ignore>Google Play.

NoteEsiaVoyager cannot be used without connection parameters to an Esia Infinity or Esia Unity server. In addition, it is designed to work with a server version 3.2.5 or higher (some features will be buggy or inaccessible if the server is in a lower version).
Connection
When you open the application for the first time, you must enter your Esia server information.
For the URL of your server, it is not necessary to add « https:// » The application does this automatically. Android security standards now only allow HTTPS connections.
The application will store the connection data in the phone's memory. The password is never saved; it is only used to create a token to connect to the server before being destroyed. It is this token that is stored in memory.
The connection information will no longer be requested, but will be automatic until the user chooses to disconnect.
SSL security
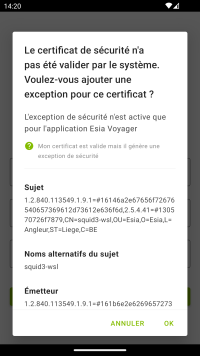
The application enables an SSL connection via a self-signed certificate (not recognised by the Android system). When the user attempts to connect to the server, a dialog box will appear displaying the certificate (which is automatically retrieved via the SSL connection) and offering the option of trusting (or not) the certificate.
This only applies to « Serveur ». It is not possible to modify the certificate « Client » certificate used for the connection. The certificate is stored by the application in secure storage and the security exception will no longer be displayed. The security exception is only valid for the EsiaVoyager application. Security exceptions can be removed by deleting all application data via the Android settings.
My certificate is valid but it generates a security exception
In some cases, a server whose SSL certificate is validated by a certification authority may nevertheless generate an exception in the EsiaVoyager application, even if no exception is generated from a web browser on the same phone. This happens when an intermediate certificate is missing from the certification chain if it is not supplied in full by the server. The web browser already knows some of the intermediate certificates used by the certification authorities and downloads the missing ones when browsing other websites. It may therefore already know the certificate used in your certification chain, even if it is not supplied by your server. The application itself does not have access to the certificates retrieved by the web browser, only to those provided by the OS.
Analysing the SSL certificate returned by the server
To check the SSL certificate returned by the server, you can use the SSL-test tool from SSL Labs.
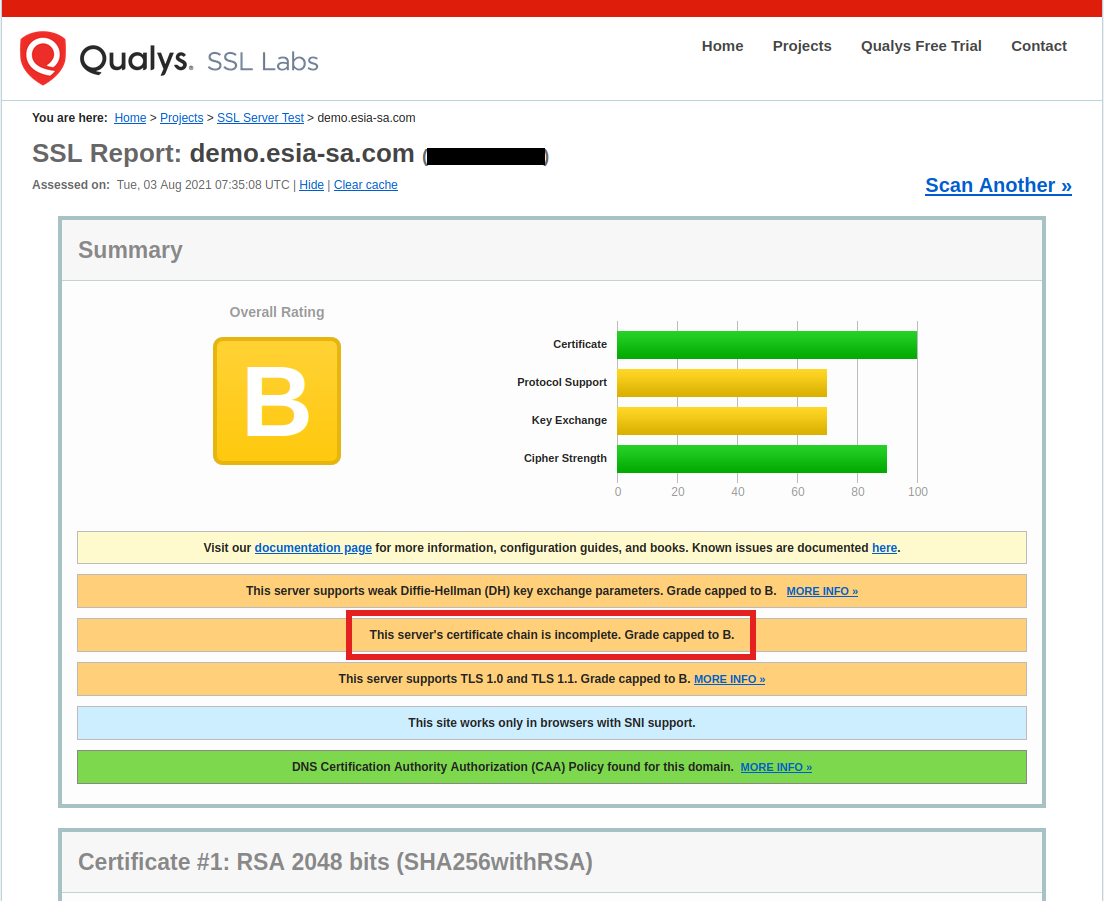
Enter the URL of your server in « Hostname », click on « Submit » and wait for the test to finish (it may take 2-3 minutes). You should then see a page like this:
If your server does not provide the complete certificate chain, you will see the message <ignore> « This server's certificate chain is incomplete ></ignore» as in the image above.
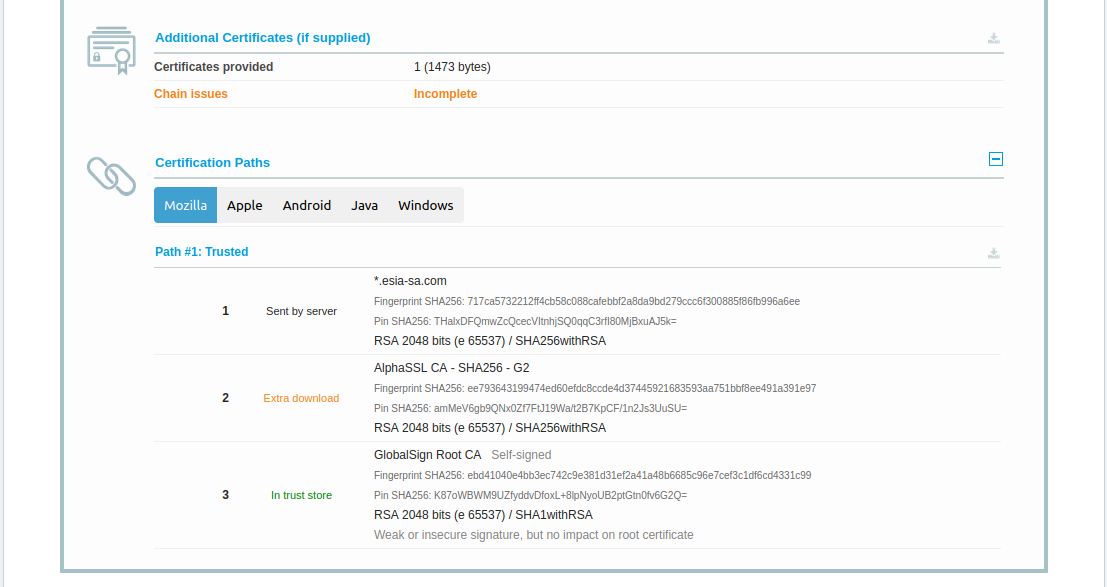
You can get more information by clicking <ignore>« Certification Paths ></ignore» at the bottom of the <ignore>« Certificate #1: … ></ignore><>
This image clearly shows that in 1 the server certificate is sent by the server, the root certificate in 3 is known by the OS, but the intermediate certificate in 2 requires an external download. This is where things get tricky for the mobile application.
No more security exceptions
You can either validate the security exception in EsiaVoyager, but you will have to do this for each client that connects to the server. Or you can modify the server so that it returns the complete certification chain instead of just the server certificate.
Tip for downloading the certification chain via Firefox
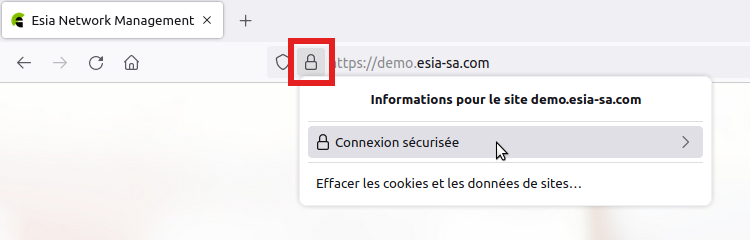
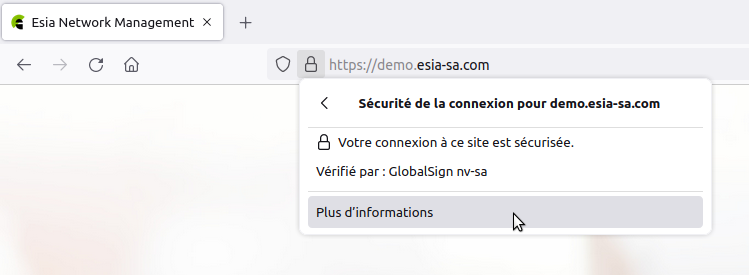
Open your Esia server page in Firefox. Click on the padlock icon to the left of the URL and then on « Connexion sécurisée »
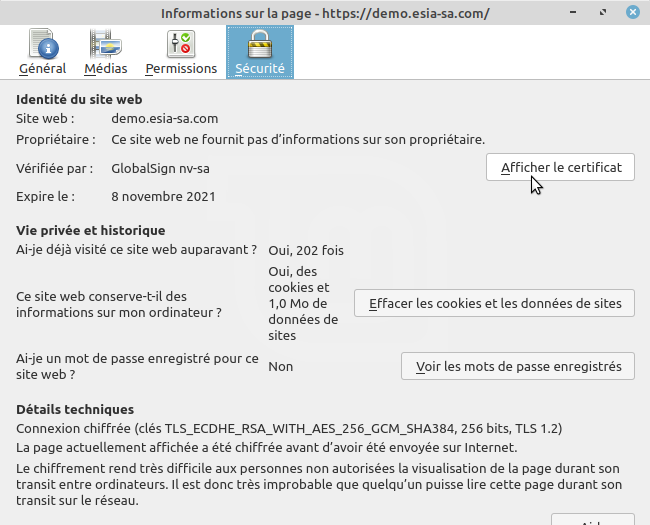
Then go to <ignore> «More information ></ignore»
Click on <ignore>«View the certificate ></ignore»
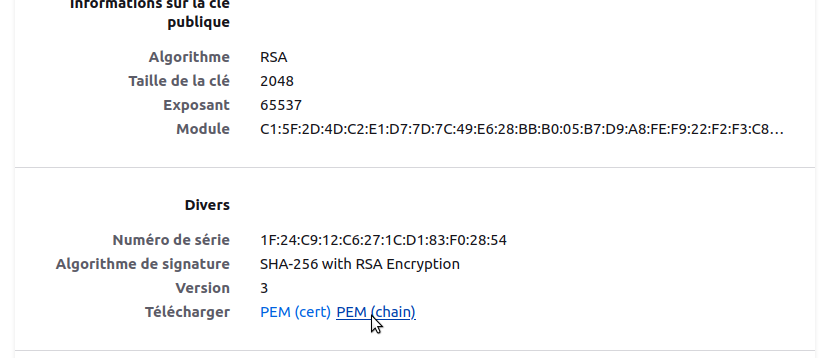
Scroll down to the « Divers » then next to « Télécharger » choose « PEM (chain) »
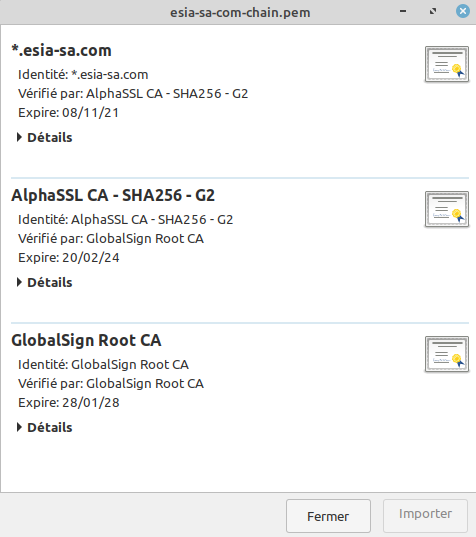
If you open the .pem file, it contains the complete certification chain.
All that remains is to replace the certificate on the server with the downloaded PEM file.
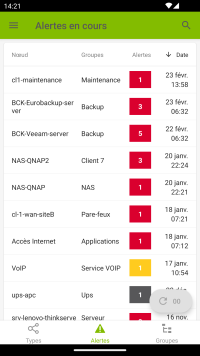
Current alerts
Once connected to the server, the application's main page displays the alerts table. This is the equivalent of the « Etat du réseau » page of the Esia web interface (click on the Alerts menu or on Node Status).
Refresh button
Pages displaying Esia data (Current Alerts, Groups, Nodes, etc.) refresh automatically every 5 minutes. This can be done manually using the refresh button. This button can be clicked one minute after the last refresh and displays the number of minutes since the last refresh.
The refresh button 2 minutes after the last page refresh:
Main menu
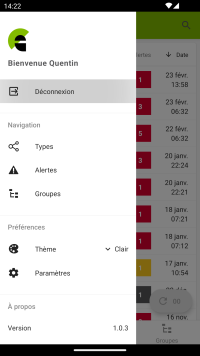
Open the left-hand menu by pressing the horizontal bars icon at the top left of the screen or by dragging it from the left of the screen.
To change user, click on the « Déconnexion » button in the left-hand menu to delete the user login details and return to the login page.
To configure the notification settings, click on the « Paramètres » button in the left-hand menu.
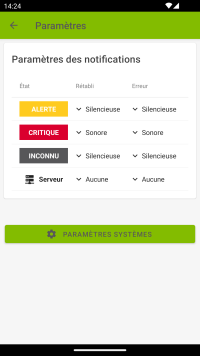
Notification settings
Notifications concern the status of services or the status of the connection between the application and the esia server. It attempts to retrieve the information every 5 minutes and compares it with the previous result to detect any differences between the number of services on alert. Obviously, if the application cannot reach the server, it cannot retrieve the status of the services.
For which events do you want to be notified?
- Restored: Notifies when the total number of errors decreases (Or server connection restored).
- Error: Notifies when the total number of errors increases (Or connection to server lost).
Notification type :
- Sound: Vibrate + Sound.
- Silent : Vibrate only.
- None : Ignore this type of event.
If several types of event are detected at the same time, the type of notification chosen will be the one with the highest priority. (1. Audible - 2. Silent)
For example, if you request an audible alert on Critical Error and a silent alert on Reset Unknown (all the rest on None). If during the first check the server contains 10 critical services and 20 unknown services. At the second check 5m later it has gone to 12 critical and 18 unknown (all other status changes will be ignored). You will receive an audible alert with the following message:
Widgets
Various widgets are available:
- Node status : the number of nodes per status (equivalent to what you see at the top right of the web interface)
- Service status : the number of services per status OK, Alert, Critical and Unknown
- Service status with maintenance : the number of services by status OK, Alert, Critical, Unknown and Maintenance
Phone settings for background tasks
Data from widgets and notifications is retrieved via a background task so that it can be retrieved even when the application is closed. Android places a whole series of restrictions on background tasks that impact their operation. It will attempt to run every 5 minutes, but it is Android that decides when it actually runs. In practice, it will run between 5 and 15 minutes, but often closer to 5 minutes.
Each manufacturer also sets a series of restrictions to limit battery use. If you want the application to run as regularly as possible and not be completely stopped by the optimization systemyou need to create an exception for EsiaVoyager in the battery optimisation settings. The method differs depending on the phone manufacturer, so I'm sharing a link to the site dontkillmyapp which provides tutorials by manufacturer and keeps them up to date.