Table of Contents
Activating PowerShell in Esia
On the Windows machine
On the Windows machine, you need to activate PowerShell remote.
- copy
Enable-PSRemoting -Force Restart-Service WinRM
You can test from your Windows machine if you have access to it in PowerShell via the command :
- copy
Enter-PSSession -ComputerName <nom de votre machine> -Credential <utilisateur> -Authentication Negotiate
Note for firewalls, the default PowerShell port is the same as for WinRM: TCP 5985.
On your Esia - Using PowerShell
Enable Powershell on your node
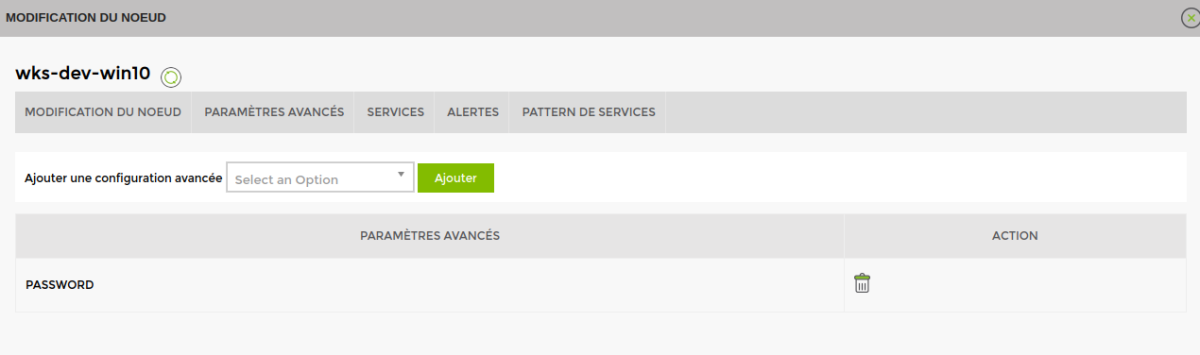
In the advanced settings of your Esia node, add the PowerShell user and password.
To do this, select the 'Password' type and click Add. Then click on the advanced parameter to configure.
Adding patterns/plugins
You can now add the following patterns and/or plugins to the node configured below:
default_pwsh_windows
Contains the plugins :
- CHECK_ICMP
- CHECK_PWSH_WINDOWS_INTERFACE: Interface bandwidth via PowerShell
- CHECK_PWSH_WINDOWS_IO: IO/disks
- CHECK_PWSH_WINDOWS_LOAD: CPU load used
- CHECK_PWSH_WINDOWS_MEM: Random Access Memory
- CHECK_PWSH_WINDOWS_STORAGE: Hard disk space used
- CHECK_PWSH_WINDOWS_TIME: Time difference between your Esia and your Windows machine.
- CHECK_PWSH_WINDOWS_UPTIME: To detect a recent restart.
Other plugins
- CHECK_PWSH_WINDOWS_SERVICE: Retrieves the status of a service.
- CHECK_PWSH_WINDOWS_SMARTCTL: Recovers the smartctl status of disks.
- CHECK_PWSH_WINDOWS_TASK: retrieves the status of a scheduled task.
- CHECK_PWSH_REMOTE : Allows an executable/script to be used on the Windows machine
Troubleshooting
Check user access rights
The user must be a member of the “Administrator” and “Remote Management Users”.
Open, « The tool for managing local users and groups ».
- copy
lusrmgr.msc
Go to « Users », then right-click « Properties » on the user concerned.

Go to the « Member of ». If the two groups are not listed, click on « Add » to add the missing groups.
Example with the group « Remote Management Users »